
- Mac command line disk utility how to#
- Mac command line disk utility mac os#
- Mac command line disk utility free#
- Mac command line disk utility mac#
You can use it to copy the contents of one partition to another, or to copy a disk image to a partition. The Restore feature allows you to copy one volume to another. The Convert and Resize Image buttons will allow you to manage that disk image from the Disk Utility window. You can then upload this encrypted DMG file to cloud storage locations or save it on unencrypted removable drives. This is particularly useful because you can encrypt that DMG file, creating an encrypted container file that can store other files. You can then mount that disk image file and write files into it.
Mac command line disk utility how to#
RELATED: How to Create an Encrypted Disk Image to Securely Store Sensitive Files on a MacĬlick the File menu in Disk Utility and use the New menu to create blank disk images or disk images containing the contents of a folder - these are.

Performing the “fastest” erase of the internal drive from recovery mode will erase everything.
Mac command line disk utility mac#
Don’t perform a secure erase on a solid-state drive, such as the ones built into modern Mac Books-that will just wear down the drive for no advantage. Note that this feature will only be useful on mechanical drives, as you shouldn’t be able to recover deleted data from a solid state drive. RELATED: How to Securely Wipe a Hard Drive on Your Mac One pass should be good enough, but you can always do a few more if you feel like it. You can use this feature to securely wipe a hard drive. Click a drive, then click the “Erase” button, then click “Security Options” to select a number of passes to overwrite the drive with.
Mac command line disk utility free#
You can also choose to only erase its free space. The Erase button allows you to erase an entire hard disk or partition. Simply click the drive you want to check, then click the “First Aid” button. Be warned that these checks can take a while, and running them on your system drive will leave you with an unresponsive computer until it’s done. This feature checks the file system for errors and attempts to correct them, all without much intervention from you. If a hard drive is acting up, Disk Utility’s First Aid function is the first thing you should try. RELATED: How, When, and Why to Repair Disk Permissions on Your Mac One of them: volumes on the same drive pool storage space, meaning you’ll see two separate drives in Finder, but won’t have to manage how much storage space each volume uses. To add a new APFS volume, simply select your system drive, and then click Edit > Add APFS in the menu bar. APFS is Apple’s new file system, the default on solid state drives as of macOS High Sierra, and it’s got all sorts of clever tricks up its sleeve. If you want to repartition your system drive, you’ll need to do this from within Recovery Mode, with one exception: APFS volumes. RELATED: APFS Explained: What You Need to Know About Apple's New File System Note: Many of these operations are destructive, so be sure you have backups first. You can also resize, delete, create, rename, and reformat partitions. You can adjust the partitioning layout scheme here. To manage your partitions, click a parent drive and select the “Partition” heading. Each “parent” drive is a separate physical drive, while each little drive icon below it is a partition on that drive. This annoyingly leaves out empty hard drives, but click Views > Show All Devices in the menu bar and you’ll see a tree of drives and their internal partitions. RELATED: How to Show Empty, Unformatted Drives in Disk Utility on macOS On the left side of the window you’ll see all mounted volumes. Partition Drives and Format Partitionsĭisk Utility shows internal drives and connected external drives (like USB drives), as well as special image files (DMG files) that you can mount and access as drives. This allows you to use Disk Utility to wipe your entire drive-or repartition it. It’s important to keep in mind that if you run the eraseDisk command, the target disk is going to lose all its data, so make sure you are erasing the proper disk.In Recovery Mode, macOS runs a special sort of recovery environment. The syntax is going to look like this: Diskutil eraseDisk JHFS+ Empty /dev/disk5s2
Mac command line disk utility mac os#
Let’s say the disk I want to erase has “/dev/disk5s2” as its identifier and I’m going to use Mac OS Extended Journaled (JHFS+) as the system format type and name it “Empty”. This is the syntax we need: Diskutil eraseDisk FILESYSTEM DISKNAME DISKIDENTIFIER Then pick a name and a system format type. Once you have found the proper drive to erase, just copy its identifier so you can use it for the next command. This is going to list all the mounted drives on your Mac. Start off by running the following command in the command line: Diskutil list Here I'll show you how you can erase and format a disk using the command line.

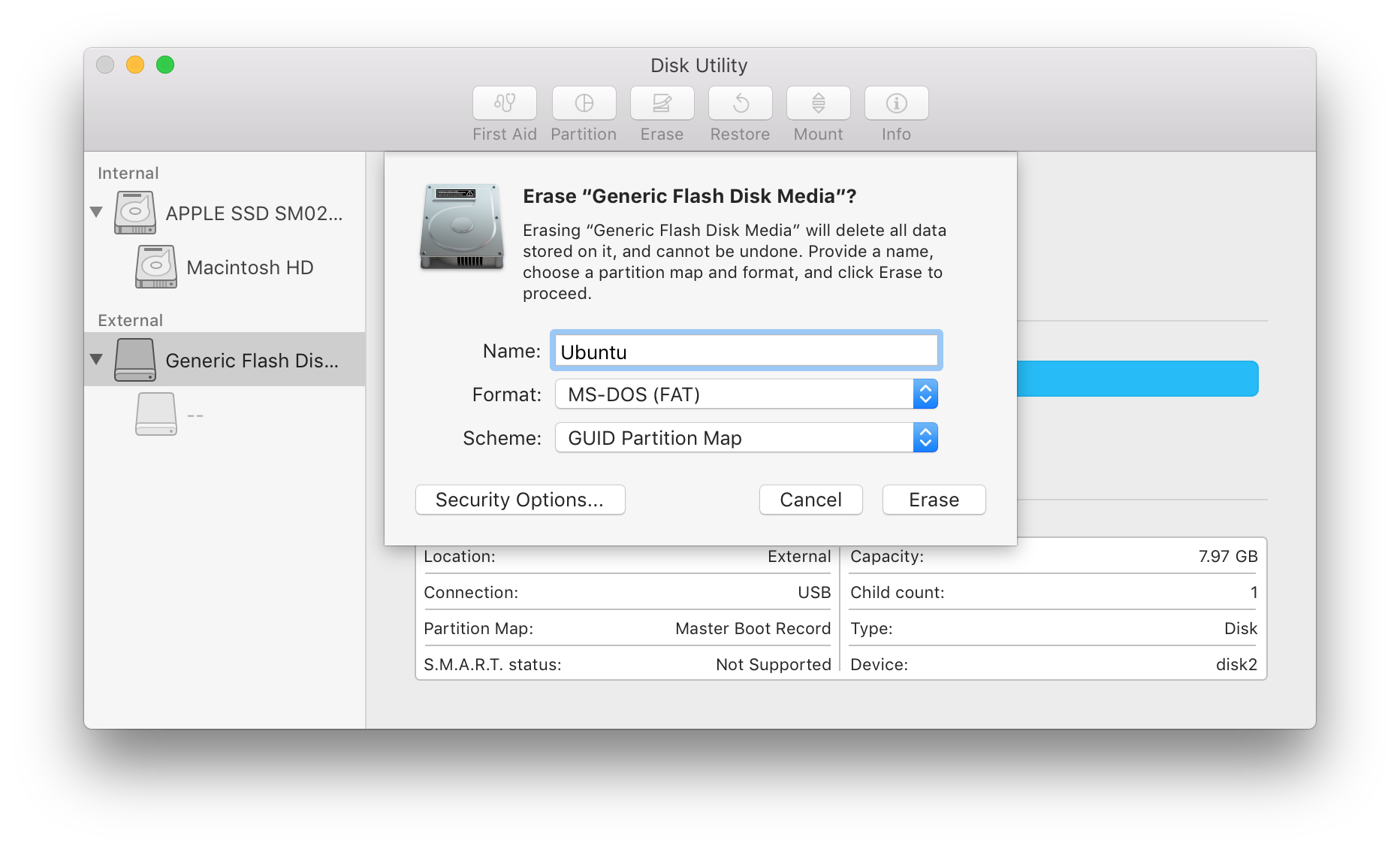
To do that, the only thing you need is a bit of precise syntax to make sure that you are erasing the proper disk.
But some Mac users might need to erase them from the command line on Mac OS. Most users use Disk Utility to erase a disk or hard drive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
